When we say the word “Australian” it conjures up images of sun, sand, fun and the laid back, lovable (NOT gullible) Aussie. But a recent study commissioned by MYFitnessPal and conducted by the Dublin City University Business School found that Australians are the most gullible when it comes to health advice on TikTok. https://www.thenewdaily.com.au/life/2024/04/11/aussies-love-dodgy-tiktok-advice
The study found that “9 out of 10 Australians have taken nutrition advice from the social media platform more than once”. Overall, two in five Australians (42%) are “trusting the social media platforms for nutrition and wellness advice”.
This is a worrying trend and one that highlights the critical importance of knowing where you can go for reliable, evidence-based health information and advice.
When ‘asking’ the internet for health information there are some trusted and reliable sources that are kept up to date with the latest information and advice – for example Musculoskeletal Health Australia’s (MHA) website (www.muscha.org.au). There are unfortunately, many websites, social media groups and platforms that contain information that does not have the research and evidence to ‘back up’ their claims. This is why being ‘health info savvy’ is so important!
A few MHA tips on where to go and how to find good health information online:
- Speak to your health care team about online information sources that they trust – check them out and bookmark them for future use
- Be clear on the question you are looking for an answer to – searching a list of symptoms is often going to have you going down a rabbit hole and into a wonderland of perhaps questionable information and health claims
- Check what evidence there is to support any claims being made – has there been research published? Who was the research done by? Who paid for the research to be done?
- Are the claims too good to be true? If you think they are, it’s a good idea to do more research, check to see if there are any other sources of information that either support or debunk the claims being made.
Another good reference is the Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care How to find good health information online (safetyandquality.gov.au) See some of their tips include:
- Look for information that is relevant to you and decide what questions you have.
- Look for trusted sources these include websites from hospitals, condition specific organisations, government, and universities.
- Look for information that you can understand as good quality health information should be clear and easy to understand as well as suggesting where to get more information and support.
- Look out for warning signs. Good quality information should not be trying to sway your opinion, sell you products, make you feel fearful or ask for personal details.
- If you connect with people online, remember other people’s experiences may not be typical and might be different from yours. Talking to other people can provide information and support but remember it’s just their opinion.
- Check the information with your health care professional. It is helpful to talk to your doctor and other healthcare providers so that you can get the information you need to make your decision.
- Ask for help if you need it to find health information online or judge its quality. You might ask a family member or friend who you trust, a healthcare provider, a local consumer organisation or a librarian.
Some other things to consider when you do a ‘search’ and to assist you to navigate (is) the CRAAP – the Currency, Relevance, Authority, Accuracy and Purpose Test.
Currency – Is this information up to date? When was it published or posted online? How old is the information? Has the information been recently revised or updated and do the links work?
Relevance – Is the information relevant to you?
- Does the information answer your questions?
- Is the site Australian?
- Does the site connect you to local services?
Authority – Is the information from an authoritative, reliable source?
- Who is the author and are they qualified to write or speak on this topic.
- Are they an expert in the area?
Accuracy – Where does the information come from and is it accurate?
- Is the information based on medical/scientific studies or personal experience?
- Is the information supported by evidence and has it been published in peer reviewed journals?
Purpose – Why was the information created and shared?
- Is the information intended to educate people, entertain or just sell you products?
- Who is funding the site?
Your health is important! Taking the time to research and evaluate information will increase your knowledge and health literacy and ensure you are in a better position to make informed health decisions.
Another important way you can help Musculoskeletal Health Australia build understanding and awareness and support others to access quality information and support is… if you’re not sure a social media post, website or discussion forum is evidence based and trustworthy, don’t share it with other people.
For quality, evidence based and reliable information and support on back pain, arthritis and other musculoskeletal conditions head to any of the following sites AND make sure you bookmark them and come back regularly to see what new information has been added:
- https://msk.org.au/
- https://versusarthritis.org/
- https://www.uptodate.com/contents/arthritis-beyond-the-basics
Please call our free, national Help Line* on 1800 263 265, or email helpline@msk.org.au for more information and support about musculoskeletal conditions, musculoskeletal health and living well.
(*Monday to Thursday 9am to 5pm, excluding public holidays)
References
https://medlineplus.gov/evaluatinghealthinformation.htm
fhttps://www.library.qut.edu.au/transcripts/craaptest.jsp
https://hslmcmaster.libguides.com/c.php?g=306752&p=5238186





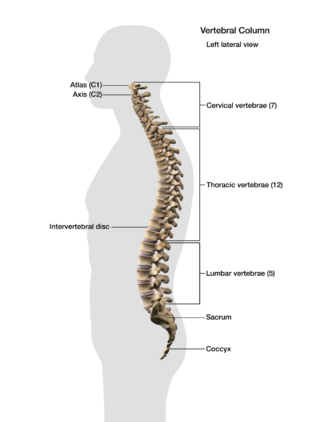 Let’s start with a look at your spine
Let’s start with a look at your spine